【强化学习】Q-Learning详解
https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/machine-learning/reinforcement-learning/2-1-general-rl/ 莫凡大神的有趣的强化学习视频通俗易懂
发现了很多RL资料搬砖过来,刚入门的可以用得上
David Silver 博士的 UCL 公开课:http://www0.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/d.silver/web/Teaching.html
DeepMind 和 UCL 的DL、RL课程:https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLqYmG7hTraZDNJre23vqCGIVpfZ_K2RZs
Sergey Levine 的DRL课程:http://rail.eecs.berkeley.edu/deeprlcourse/
OpenAI 的 Spinning Up in Deep RL:https://blog.openai.com/spinning-up-in-deep-rl/
关于深度强化学习良心paper:https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.06339
1、算法思想
QLearning是强化学习算法中value-based的算法,Q即为Q(s,a)就是在某一时刻的 s 状态下(s∈S),采取 动作a (a∈A)动作能够获得收益的期望,环境会根据agent的动作反馈相应的回报reward r,所以算法的主要思想就是将State与Action构建成一张Q-table来存储Q值,然后根据Q值来选取能够获得最大的收益的动作。
| Q-Table | a1 | a2 |
|---|---|---|
| s1 | q(s1,a1) | q(s1,a2) |
| s2 | q(s2,a1) | q(s2,a2) |
| s3 | q(s3,a1) | q(s3,a2) |
2、公式推导
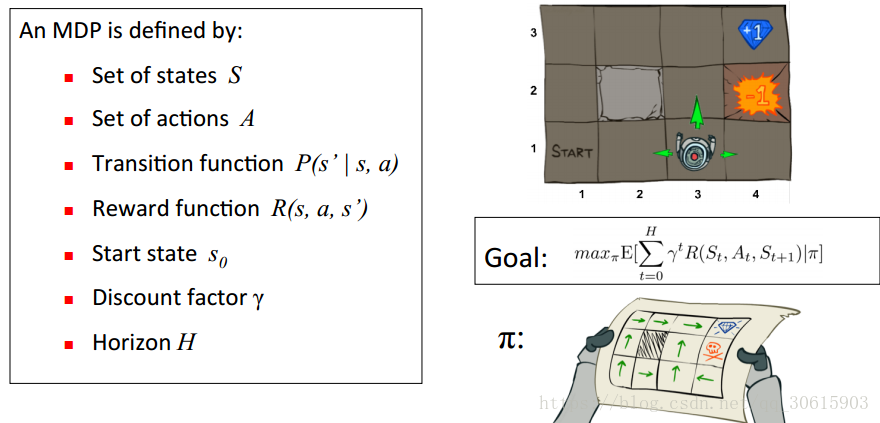
举个例子如图有一个GridWorld的游戏从起点出发到达终点为胜利掉进陷阱为失败。智能体(Agent)、环境状态(environment)、奖励(reward)、动作(action)可以将问题抽象成一个马尔科夫决策过程,我们在每个格子都算是一个状态 s t s_t st , π(a|s)在s状态下采取动作a策略 。 P(s’|s,a)也可以写成 P s s ′ a P_{ss'}^a Pss′a为在s状态下选择a动作转换到下一个状态s’的概率。R(s’|s,a)表示在s状态下采取a动作转移到s’的奖励reward,我们的目的很明确就是找到一条能够到达终点获得最大奖赏的策略。
所以目标就是求出累计奖励最大的策略的期望:
Goal: max π E [ ∑ t = 0 H γ t R ( S t , A t , S t + 1 ) ∣ π ] \max_πE[\sum_{t=0}^{H}γ^tR(S_t,A_t,S_{t+1}) | π] maxπE[∑t=0HγtR(St,At,St+1)∣π]
Qlearning的主要优势就是使用了时间差分法TD(融合了蒙特卡洛和动态规划)能够进行离线学习, 使用bellman方程可以对马尔科夫过程求解最优策略
贝尔曼方程
通过bellman方程求解马尔科夫决策过程的最佳决策序列,状态值函数 V π ( s ) V_\pi(s) Vπ(s)可以评价当前状态的好坏,每个状态的值不仅由当前状态决定还要由后面的状态决定,所以状态的累计奖励求期望就可得出当前s的状态值函数V(s)。bellman方程如下
V π ( s ) = E ( U t ∣ S t = s ) V_π(s) = E(U_t|S_t = s) Vπ(s)=E(Ut∣St=s)
V π ( s ) = E π [ R t + 1 + γ [ R t + 2 + γ [ . . . . . . . ] ] ∣ S t = s ] V_π(s) = E_π[R_{t+1}+γ[R_{t+2} + γ[.......]]|S_t = s] Vπ(s)=Eπ[Rt+1+γ[Rt+2+γ[.......]]∣St=s]
V π ( s ) = E π [ R t + 1 + γ V ( s ′ ) ∣ S t = s ] V_π(s) = E_π[R_{t+1}+γV(s')|S_t = s] Vπ(s)=Eπ[Rt+1+γV(s′)∣St=s]
最优累计期望可用 V ∗ ( s ) V^*(s) V∗(s)表示,可知最优值函数就是 V ∗ ( s ) = m a x π V π ( s ) V^*(s)=max_πV_\pi(s) V∗(s)=maxπVπ(s)
V ∗ ( s ) = max π E [ ∑ t = 0 H γ t R ( S t , A t , S t + 1 ) ∣ π , s 0 = s ] V^*(s)=\max_πE[\sum_{t=0}^{H}γ^tR(S_t,A_t,S_{t+1}) | π,s_0=s] V∗(s)=maxπE[∑t=0HγtR(St,At,St+1)∣π,s0=s]
Q(s,a)状态动作值函数
q π ( s , a ) = E π [ r t + 1 + γ r t + 2 + γ 2 r t + 3 + . . . . ∣ A t = a , S t = s ] q_π(s,a) = E_π[r_{t+1}+γr_{t+2}+γ^2r_{t+3}+....|A_t=a,S_t=s] qπ(s,a)=Eπ[rt+1+γrt+2+γ2rt+3+....∣At=a,St=s]
q π ( s , a ) = E π [ G t ∣ A t = a , S t = s ] q_π(s,a) = E_π[G_t|A_t=a,S_t=s] qπ(s,a)=Eπ[Gt∣At=a,St=s]
其中 G t G_t Gt是t时刻开始的总折扣奖励,从这里我们能看出来 γ衰变值对Q函数的影响,γ越接近于1代表它越有远见会着重考虑后续状态的的价值,当γ接近0的时候就会变得近视只考虑当前的利益的影响。所以从0到1,算法就会越来越会考虑后续回报的影响。
q π ( s , a ) = E π [ R t + 1 + γ q π ( S t + 1 , A t + 1 ) ∣ A t = a , S t = s ] q_π(s,a) = E_π[R_{t+1}+γq_π(S_{t+1},A_{t+1})|A_t=a,S_t=s] qπ(s,a)=Eπ[Rt+1+γqπ(St+1,At+1)∣At=a,St=s]
最优价值动作函数 Q ∗ ( s , a ) = m a x π Q ∗ ( s , a ) Q^*(s,a)=max_\pi Q^*(s,a) Q∗(s,a)=maxπQ∗(s,a),打开期望如下
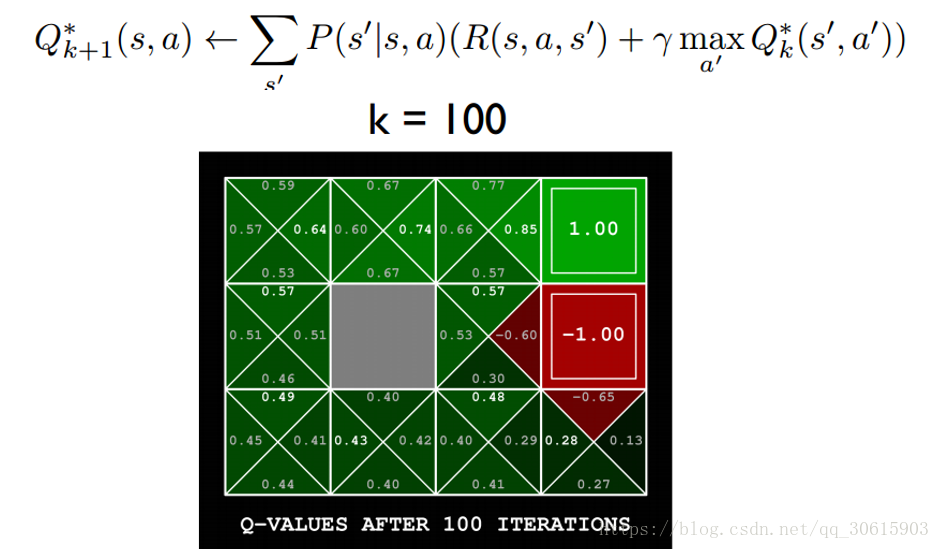
Q ∗ ( s , a ) = ∑ s ′ P ( s ′ ∣ s , a ) ( R ( s , a , s ′ ) + γ max a ′ Q ∗ ( s ′ , a ′ ) ) Q^*(s,a)=\sum_{s'} P(s'|s,a)(R(s,a,s')+γ\max_{a'}Q^*(s',a')) Q∗(s,a)=∑s′P(s′∣s,a)(R(s,a,s′)+γmaxa′Q∗(s′,a′))
Bellman方程实际上就是价值动作函数的转换关系
V π ( s ) = ∑ a ∈ A π ( a ∣ s ) q π ( s , a ) V_π(s) = \sum_{a∈A}π(a|s)q_π(s,a) Vπ(s)=∑a∈Aπ(a∣s)qπ(s,a)
q π ( s , a ) = R s a + γ ∑ s ′ ∈ S P s s ′ a V π ( s ′ ) q_π(s,a) = R_s^a + γ\sum_{s'∈S}P_{ss'}^aV_π(s') qπ(s,a)=Rsa+γ∑s′∈SPss′aVπ(s′)
V π ( s ) = ∑ a ′ ∈ A π ( a ∣ s ) [ R s a + γ ∑ s ′ P s s ′ a V π ( s ′ ) ] V_π(s)=\sum_{a'∈A}π(a|s)[R_s^a+γ\sum_{s'}P_{ss'}^aV_π(s')] Vπ(s)=∑a′∈Aπ(a∣s)[Rsa+γ∑s′Pss′aVπ(s′)]
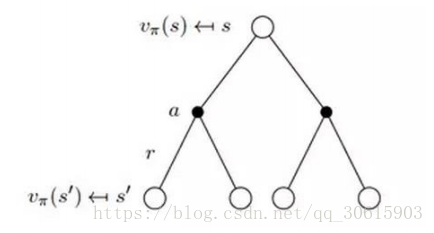
根据下图更直观的了解V(s)与Q(s,a)的关系
时间差分法 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_30615903/article/details/80821061
时间差分方法结合了蒙特卡罗的采样方法和动态规划方法的bootstrapping(利用后继状态的值函数估计当前值函数)使得他可以适用于model-free的算法并且是单步更新,速度更快。值函数计算方式如下
V ( s ) ← V ( s ) + α ( R t + 1 + γ V ( s ′ ) − V ( s ) ) V(s)←V(s)+\alpha (R_{t+1}+\gamma V(s')-V(s)) V(s)←V(s)+α(Rt+1+γV(s′)−V(s))
其中 R t + 1 + γ V ( s ′ ) R_{t+1}+\gamma V(s') Rt+1+γV(s′)被称为TD目标, δ t = R t + 1 + γ V ( s ′ ) − V ( s ) \delta_t=R_{t+1}+\gamma V(s')-V(s) δt=Rt+1+γV(s′)−V(s) 称为TD偏差。
3、更新公式
根据以上推导可以对Q值进行计算,所以有了Q值我们就可以进行学习,也就是Q-table的更新过程,其中α为学习率γ为奖励性衰变系数,采用时间差分法的方法进行更新。
Q ( s , a ) ← Q ( s , a ) + α [ r + γ m a x a ′ Q ( s ′ , a ′ ) − Q ( s , a ) ] Q(s,a) ← Q(s,a) + α[r + γmax_{a'}Q(s',a')-Q(s,a)] Q(s,a)←Q(s,a)+α[r+γmaxa′Q(s′,a′)−Q(s,a)]
上式就是Q-learning更新的公式,根据下一个状态s’中选取最大的 Q ( s ′ , a ′ ) Q(s',a') Q(s′,a′)值乘以衰变γ加上真实回报值最为Q现实,而根据过往Q表里面的Q(s,a)作为Q估计。

4、实现代码
代码来自网上各路大神的源码,非原创,据反映没图片跑不通,所以建了个github,https://github.com/xshura/reinforcement_learning
Q-Learning agent
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import randomfrom environment import Envfrom collections import defaultdictclass QLearningAgent: def __init__(self, actions): # actions = [0, 1, 2, 3] self.actions = actions self.learning_rate = 0.01 self.discount_factor = 0.9 self.epsilon = 0.1 self.q_table = defaultdict(lambda: [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]) # 采样 <s, a, r, s'> def learn(self, state, action, reward, next_state): current_q = self.q_table[state][action] # 贝尔曼方程更新 new_q = reward + self.discount_factor * max(self.q_table[next_state]) self.q_table[state][action] += self.learning_rate * (new_q - current_q) # 从Q-table中选取动作 def get_action(self, state): if np.random.rand() < self.epsilon: # 贪婪策略随机探索动作 action = np.random.choice(self.actions) else: # 从q表中选择 state_action = self.q_table[state] action = self.arg_max(state_action) return action @staticmethod def arg_max(state_action): max_index_list = [] max_value = state_action[0] for index, value in enumerate(state_action): if value > max_value: max_index_list.clear() max_value = value max_index_list.append(index) elif value == max_value: max_index_list.append(index) return random.choice(max_index_list)if __name__ == "__main__": env = Env() agent = QLearningAgent(actions=list(range(env.n_actions))) for episode in range(1000): state = env.reset() while True: env.render() # agent产生动作 action = agent.get_action(str(state)) next_state, reward, done = env.step(action) # 更新Q表 agent.learn(str(state), action, reward, str(next_state)) state = next_state env.print_value_all(agent.q_table) # 当到达终点就终止游戏开始新一轮训练 if done: break环境部分
import timeimport numpy as npimport tkinter as tkfrom PIL import ImageTk, Imagenp.random.seed(1)PhotoImage = ImageTk.PhotoImageUNIT = 100HEIGHT = 5WIDTH = 5class Env(tk.Tk): def __init__(self): super(Env, self).__init__() self.action_space = ['u', 'd', 'l', 'r'] self.n_actions = len(self.action_space) self.title('Q Learning') self.geometry('{0}x{1}'.format(HEIGHT * UNIT, HEIGHT * UNIT)) self.shapes = self.load_images() self.canvas = self._build_canvas() self.texts = [] def _build_canvas(self): canvas = tk.Canvas(self, bg='white', height=HEIGHT * UNIT, width=WIDTH * UNIT) # create grids for c in range(0, WIDTH * UNIT, UNIT): # 0~400 by 80 x0, y0, x1, y1 = c, 0, c, HEIGHT * UNIT canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1) for r in range(0, HEIGHT * UNIT, UNIT): # 0~400 by 80 x0, y0, x1, y1 = 0, r, HEIGHT * UNIT, r canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1) # add img to canvas self.rectangle = canvas.create_image(50, 50, image=self.shapes[0]) self.triangle1 = canvas.create_image(250, 150, image=self.shapes[1]) self.triangle2 = canvas.create_image(150, 250, image=self.shapes[1]) self.circle = canvas.create_image(250, 250, image=self.shapes[2]) # pack all canvas.pack() return canvas def load_images(self): rectangle = PhotoImage( Image.open("../img/rectangle.png").resize((65, 65))) triangle = PhotoImage( Image.open("../img/triangle.png").resize((65, 65))) circle = PhotoImage( Image.open("../img/circle.png").resize((65, 65))) return rectangle, triangle, circle def text_value(self, row, col, contents, action, font='Helvetica', size=10, style='normal', anchor="nw"): if action == 0: origin_x, origin_y = 7, 42 elif action == 1: origin_x, origin_y = 85, 42 elif action == 2: origin_x, origin_y = 42, 5 else: origin_x, origin_y = 42, 77 x, y = origin_y + (UNIT * col), origin_x + (UNIT * row) font = (font, str(size), style) text = self.canvas.create_text(x, y, fill="black", text=contents, font=font, anchor=anchor) return self.texts.append(text) def print_value_all(self, q_table): for i in self.texts: self.canvas.delete(i) self.texts.clear() for i in range(HEIGHT): for j in range(WIDTH): for action in range(0, 4): state = [i, j] if str(state) in q_table.keys(): temp = q_table[str(state)][action] self.text_value(j, i, round(temp, 2), action) def coords_to_state(self, coords): x = int((coords[0] - 50) / 100) y = int((coords[1] - 50) / 100) return [x, y] def state_to_coords(self, state): x = int(state[0] * 100 + 50) y = int(state[1] * 100 + 50) return [x, y] def reset(self): self.update() time.sleep(0.5) x, y = self.canvas.coords(self.rectangle) self.canvas.move(self.rectangle, UNIT / 2 - x, UNIT / 2 - y) self.render() # return observation return self.coords_to_state(self.canvas.coords(self.rectangle)) def step(self, action): state = self.canvas.coords(self.rectangle) base_action = np.array([0, 0]) self.render() if action == 0: # up if state[1] > UNIT: base_action[1] -= UNIT elif action == 1: # down if state[1] < (HEIGHT - 1) * UNIT: base_action[1] += UNIT elif action == 2: # left if state[0] > UNIT: base_action[0] -= UNIT elif action == 3: # right if state[0] < (WIDTH - 1) * UNIT: base_action[0] += UNIT # 移动 self.canvas.move(self.rectangle, base_action[0], base_action[1]) self.canvas.tag_raise(self.rectangle) next_state = self.canvas.coords(self.rectangle) # 判断得分条件 if next_state == self.canvas.coords(self.circle): reward = 100 done = True elif next_state in [self.canvas.coords(self.triangle1), self.canvas.coords(self.triangle2)]: reward = -100 done = True else: reward = 0 done = False next_state = self.coords_to_state(next_state) return next_state, reward, done # 渲染环境 def render(self): time.sleep(0.03) self.update()